CSS Design Notes
CSS Framework Key Points
- Design tokens.
- Content.
- Centering.
- Spacing.
- Color and contrast.
- Balance (position).
- Primary and secondary color.
- Custom text (font).
- Font family.
- Images and links.
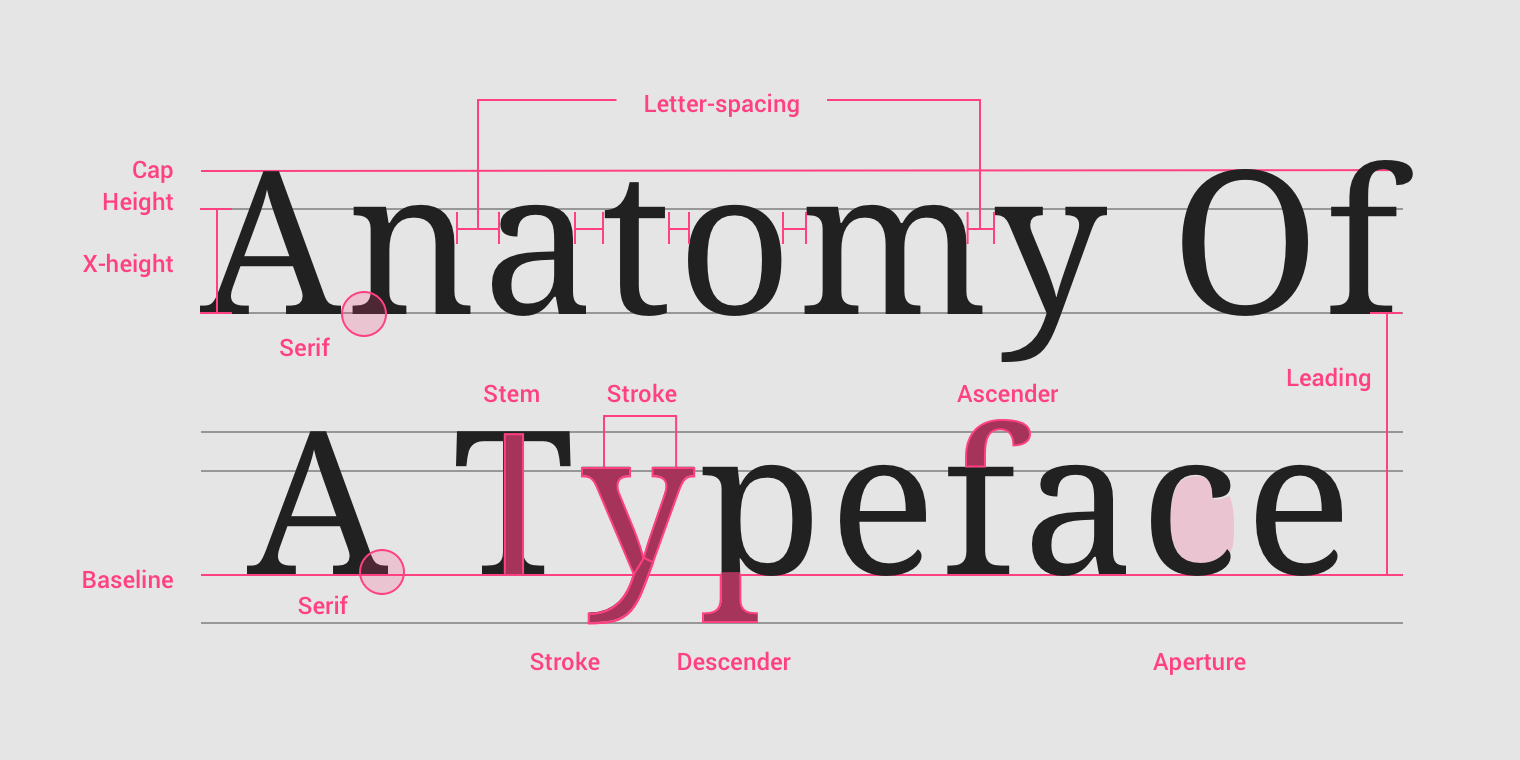
Typography Principles
- The typeface (font-family).
- Type (modular) scale.
- Responsiveness of the text (size unit and breakpoints).
- Spacing and vertical rhythm.
- Colors (theming).
Refer to: font-family, font-size, spacing, color.
Typography Properties
Font Size
- Set a base-size.
- Multiples of base-size.
- Use
remfor most font-size, useemfor some spacing (needing responsive design). remis better.emfor responsive layout: e.g layer2 font based-on layer1 font in dropdown menu.- Make text legible: at least
16px.
$xs: $base / $ratio / $ratio;
$sm: $base / $ratio;
$md: $base;
$lg: $base * $ratio;
$xl: $base * $ratio * ratio;
Spacing
Make text breathe:
margin/padding: at least15px.line-height:1.4.word-spacing.letter-spacing.- 60-100 characters per line.
Vertical Rhythms
Keep vertical spaces between elements on a page consistent (and relative) to each other:
- Set the vertical white space between elements to a multiple of base-size.
- Set the line-height of all text elements to a multiple of base-size.
- Set
margin-topandmargin-bottomto<h1>~<h6>/<hr>elements setmargin-bottomto normal elements.
Line Length
The optimal line length for body text is 50–75 characters:
- Shorter or longer line lengths can hurt readability.
.line-length {
margin-top: 2em;
line-height: 1.5em;
letter-spacing: 0.12em;
word-spacing: 0.16em;
}
Table Typography
- Remove fills, grid lines, border and bolding.
- Left-align text, right-align numbers and align headings with data.
- Put white space to work to group and separate.
Typography Reference
- Understanding typography guide.
- Practical typography guide.
- Golden rules of web typography reference.
- Typeface font matrix.
Responsive Design
- Mobile first:
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px). - Media query.
- Fluid layout.
- Flexible image.
Mobile Viewport
Disable mobile browser auto scale:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
Responsive Font
rem/emfont size.
Responsive Length
vw.vh.vmin:min(vw, vh).vmax:max(vw, vh).
Responsive Size
- Size in
emif the property scales according to it'sfont-size: e.g buttonpadding. - Modular font size:
Size in
emif thefont-sizeshould be modular (relative to it's context/parent). - Size everything else in
rem(include@mediaqueries).
/* scales to self font-size */
.container {
margin-top: 1.2em;
}
/* modular font size */
.container {
font-size: 1.2rem;
}
.container p {
font-size: 1em;
}
.container small {
font-size: 0.9em;
}
Responsive Box
Responsive Width and Height
min-height.max-height.min-width.max-width.
/* responsive images */
img {
display: block;
max-width: 100%;
}
Image Display
Image display set to inline default.
Responsive Inline Box
use inline-box with width
.element {
display: inline-box;
width: 80%;
}
Responsive Flex Box
.box {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.box > .item {
flex: 1;
}
Responsive Grid Box
.box {
display: grid;
grid-template-areas:
'hd'
'st1'
'.'
'st2'
'.';
grid-template-columns: 1fr;
}
@media only screen and (width >= 768px) {
.box {
grid-template-areas:
'hd hd'
'st1 .'
'. st2';
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr;
}
}
@media only screen and (width >= 1280px) {
.box {
grid-template-areas:
'hd hd hd'
'st1 . st2'
'st1 . st2';
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr;
}
}
@media only screen and (width >= 1536px) {
.box {
grid-template-areas:
'hd st1 . st2'
'hd st1 . st2';
grid-template-columns: 20% 1fr 1fr 1fr;
}
}
Responsive Image
.responsive-image {
display: block;
max-width: 100%;
height: auto;
}
<picture>
<source srcset="mdn-logo-wide.png" media="(min-width: 600px)" />
<img src="mdn-logo-narrow.png" alt="MDN" />
</picture>
<img src="x-small.png" srcset="x-small.png 300w, small.png 400w, medium.png
600w, large.png 800w, x-large.png 1200w" sizes="(min-width: 70em) 12.6875em,
(min-width: 50em) calc(25vw * 0.95 - 2.75em), (min-width: 35em) calc(95vw / 2 -
4.125em), calc(95vw - 1.375em)" " alt="Dummy Image" />
Responsive Table
table {
width: 100%;
}
@media (width <= 30em) {
table,
thead,
tbody,
tr,
th,
td {
display: block;
}
tr {
margin-bottom: 1em;
}
/* 隐藏表头 */
thead tr {
position: absolute;
top: -9999px;
left: -9999px;
}
}
Design Principles
Cicada Principle
禅原则:
当用户注意到一个有辨识度的特征 (比如木纹上的节疤) 在以固定的规律循环重复时, 那它试图营造的自然随机性就会立刻崩塌. 使用 CSS 实现形状时, 应尽可能地重现大自然的随机性.
Fitts Law
费茨定律:
人机交互和人体工程学中人类活动的模型, 它预测了从任意位置快速移动到一个目标位置所需的时间, 由 2 个位置的距离(D)和目标大小(S)有关, 正比于 D, 反比于 S:
- 关联性强的 UI 放置在一起.
- 大拇指点击热区.
- 屏幕边界视为无限大 (容易到达).
- 关机滑动距离长.
- 利用透明边框或伪元素扩大可点击区域 (hit area).
米勒定律
人的短时记忆能力广度为 7±2 个信息块:
- 手机号/银行卡号/超大数字分段放置, 信息分层 e.g
134 9999 9999,999, 999, 999. - 文章布局时增大段落间 margin, 改变部分文字的粗细/字体/颜色.
- 导航/选项卡不超过 9 个 (超过 9 个可使用 dropdown/subMenu).
席克定律
用户所面临的选择数量越多, 做出选择所花费的时间就越长, 在人机交互的界面中选项越多, 意味着用户做出决策的时间越长:
- 减少选项并提供默认值.
- 分类分层.
- 分步分页 (大部分手机应用注册界面).
泰斯勒定律
泰斯勒定律又称复杂性守恒定律, 该定律认为每一个过程都有其固有的复杂性, 这个复杂性存在一个临界点, 超过了这个点就不能再简化了, 你只能将固有的复杂性从一个地方移动到另外一个地方:
- 智能手机: 按键的复杂度转为手机操作系统的复杂度.
- 智能推荐: 用户自己选择筛选条件的复杂度转为人工智能算法的复杂度.
Components Design Principles
- UX Checklist
- Components Checklist
- Accordion
- Responsive Configurator
- DateTime Picker
- Feature Comparison Table
- Slider
- Birthday Picker
- Mega Dropdown
- Frozen Filter
- Disabled Button
- Infinite Scroll
- Breadcrumbs
- Push Notification
- Carousel
- Navigation
- Language Selector
- Data Visualization
- Pricing Page
- Authentication Page
- Back Button
- Error Message
- Inline Validation
HomePage User Experience
UX research point out that:
- Feature a Broad Range of Product Types (6% Don’t).
- Avoid Overly Aggressive and Distracting Ads (59% Don’t).
- Implement Carousels Carefully (75% Don’t).
- Assist the Selection of a Well-Defined Scope (62% Don’t).
- Invest in Bespoke Imagery and Design (19% Don’t).
- Make the Search Field Immediately Obvious (22% Don’t).
- Implement Country & Language Selection Carefully (35% Don’t).
- Ensure Visual Hit Areas Match the Actual Hit Areas (43% Don’t).
Form Design Principles
Buttons Placement Principles
- Align the primary button to the left edge of the inputs.
- Put the back button above the form.
- Put tangentially related actions above the form.
- Place extra buttons based on what they do.
- In some single field forms put the button next to the input (e.g
searchbutton). - Put buttons on multi select forms above the form.